Maven Tutorial: Apache Maven is a tool that is often used in many projects. Let’s learn about this tool from the basics, including how to install Maven, set it up on Windows and Mac, create a Maven project and other concepts.
What Is The Purpose Of Maven?
Earlier, when we were working on projects, we had to download the dependencies, add them to our project’s classpath, compile the source code, and run the tests. Finally, package the code into files like JARs or ZIPs and then put these files on a server or repository.
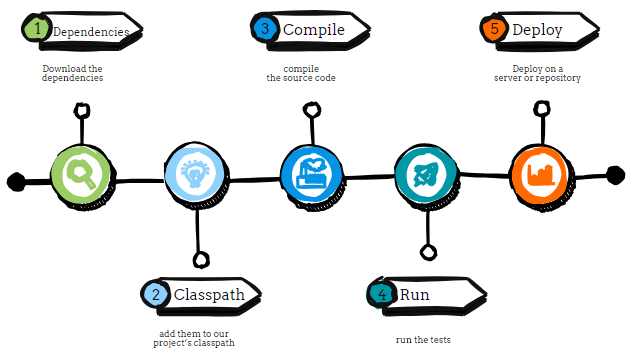
Using Maven can make this easier. It will take care of the above many tasks automatically, reducing the chance of mistakes. For example, Maven can create the initial folders for a project, compile the code, test it, package it for deployment, and deploy it.
| Post On: | Maven tutorial |
| Post Type: | Maven |
| Published On: | www.softwaretestingo.com |
| Applicable For: | Freshers & Experience |
Why do we need Maven?
If you are working on Java projects, you often need some libraries or JAR files. In the past, you had to download these and update your project’s software manually. This was a lot of work, so there was a need for a better tool to handle these tasks automatically.
If you are looking for such a thing, then Maven is the answer for managing these dependencies. You just list the libraries and software versions you need in a file called pom.xml, and Maven does the rest. Maven helps in other ways, too:
- Easy Project Setup: Maven provides templates, called archetypes, that make it easier to set up a project.
- Dependency Management: Maven automatically updates, downloads, and checks the compatibility of the dependencies you need. It also alerts you to any problems.
- Repository: Maven can get project dependencies from your local files or download them from public repositories on the internet.
What is Maven?
Maven is a powerful build automation tool that can be used for Java-based projects. It was developed by the Apache Software Foundation and was formerly part of the Jakarta project. Maven also provides two critical aspects of building software, that are:
Maven can help you manage your projects by downloading Java libraries and Maven plug-ins from one or more repositories. It stores these in a local cache so that the artifacts of your local projects can be updated as well.
Additionally, Maven is versatile and can also help you build and manage projects written in C#, Ruby, Scala, and other languages.
The POM file is an XML document that contains all the information Maven needs to build a project. This includes things like dependencies, source directories, plugin goals, and so on.
When you execute a Maven command, you’re actually giving it a POM file to use. Maven reads this file to know what to do.
When should someone use Maven?
- If, on your project, you are using many dependencies.
- When the used dependency versions are updated frequently.
- Continuous builds, integration, and testing can be easily handled by using Maven.
- When there is a need to generate documentation from source code, try compiling the code and packaging it into JAR or ZIP files.
Apache Maven Tutorial
Maven Repositories
Here, we are trying to share a little bit of information about the frequently used terms of Maven.
Maven Local Repository: This is the place where Maven stores all of its project-related jars files, libraries, and dependencies. By default, this folder is named ‘.m2’ and is located in ‘Libraries\Documents.m2’.
Maven Central Repository: The Maven Central Repository is the go-to location for all your project dependency needs. If a required library isn’t found in the local repository, Maven will look to the Central Repository for downloading it into the local repository.
Conclusion:
I hope you have got a clear idea about the Maven build and project automation tool. Also, in this Maven Tutorial, we have discussed what Maven is and why we are using Maven in our project. If you still have any concerns or doubts, then let us know in the comment section.
